Electrical Power in Circuits
What you should know
⇒ The rate at which energy is transferred by an appiance from one energy store to another is called the power
⇒ Power, P, potential difference, V, and current, I, are related by the equation: P = I x V
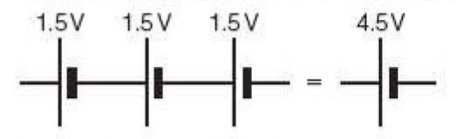
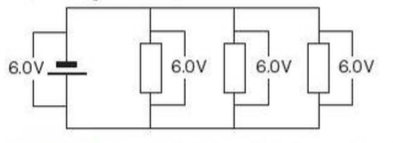
⇒ The potential difference provided by cells connected in series is the sum of the potential difference of each cell (depending on the direction in which they are connected)
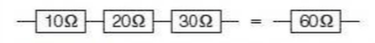
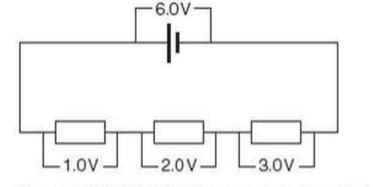
⇒ For components connected in series:
- The total resistance is the sum of the resistance of each component
- There is the same current through each component
- The total potential difference of the supply is shared between the components
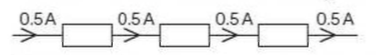
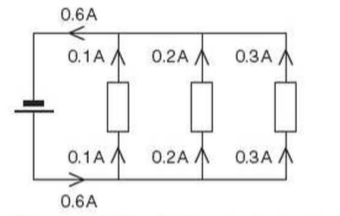
⇒ For components connected in parallel:
- The potential difference across each component is the same
- The total current through the whole circuit is the sum of the currents through the separate components
⇒ The resistance of a light-dependant resistor (LDR) decreases as light intensity increases
⇒ The resistance of a thermistor decreases as the temperature increases
Summary
⇒ One of the most fundamental properties that electronic engineers need to consider when designing electrical devices is the power transferred by the circuit in the device
- High power consumption requires specialist cooling systems and, if the device is battery powered, high battery capacity
- Minimising power consumption reduces costs and bulk
⇒ The electrical power transferred by a circuit is the sum of all the power transferred by the individual electrical components in the circuit
- The electrical power transferred by a component is related to the current flowing through it and the potential difference across it
⇒ The general definition of power is: power = rate of doing work or transferring energy
⇒ So, in an electrical context, electrical power can be defined as the rate of doing electrical work
⇒ The electrical power transferred by a component can be determined by using the current, the potential difference, and resistance of the component, and there are several equations that can be used to calculate this power
- These equations are produced by rearranging the basic equations for electrical current, potential difference and the definition of resistance:


Extra
⇒ Also see our notes on: